What is an OH&S Risk Analysis?
 It is important to understand what the Risk Analysis involves, and what information it will provide. Typically, the risk analysis process starts with the preparation of process flow diagrams to describe the activities/steps. It follows with the initial reviews and the completion of checklists to identify hazards that may be present in your workplaces. It continues with the use of an 8-column risk management worksheet that takes you through a series of information gathering actions designed to assist in deciding whether or not a hazard and/or process step is at risk and concludes with taking appropriate corrective actions.
It is important to understand what the Risk Analysis involves, and what information it will provide. Typically, the risk analysis process starts with the preparation of process flow diagrams to describe the activities/steps. It follows with the initial reviews and the completion of checklists to identify hazards that may be present in your workplaces. It continues with the use of an 8-column risk management worksheet that takes you through a series of information gathering actions designed to assist in deciding whether or not a hazard and/or process step is at risk and concludes with taking appropriate corrective actions.
The most important tool for this initiative is the worksheet for OH&S Risk Analysis is the Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Determining Controls. The 8-column worksheet is used to cover the office/administrative and the plant/manufacturing workplaces. The Worksheets provide the implementation team with a report of the findings and tell them what areas of your workplaces need corrections. The team will now know how to manage the health and safety risks.
Scheduling and Conducting the OH&S Risk Analysis
Review the project plan: Who did you identify to conduct the analyses?
Schedule time to analyze the risks for the office and plant workplaces.
Conducting the Analyses
Use the 8-column worksheet to cover the both the office/administrative and the plant/manufacturing workplaces.
- Column 1 — Transfer from the initial review checklists, the items that need attention.
- Column 2 — Identify what may be present or could be introduced as a risk.
- Column 3 — Describe the risks that may exist or could be introduced.
- Column 4 — Assess the significance of the described risk. A general approach is:
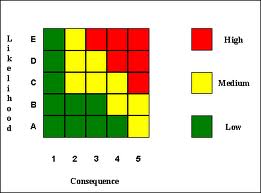
- Indicate the severity as L for low, M for medium, H for high.
- Indicate the likelihood of occurrence as Low, Medium or High.
- When both the severity and likelihood are high, the significance is high, the hazard presents a risk, it requires attention and corrective action is required.
- When one or both severity and likelihood are indicated as medium, additional reviews are required and resulting actions justified with inputs in columns 5 & 6.
- Column 5 — For Low, Medium, and High significance risks, indicate if the risk can be eliminated or reduced in a next step in the process.
- Column 6 — For all risks, describe what controls are in place to reduce or eliminate the risk.
- Column 7 — The Team considers the inputs from columns 1 through 6 and indicates with a NO or a YES whether or not the hazard / item / process step is a risk.
- Column 8 — With a NO decision, a corrective action request (CAR) is not needed and N/A is indicated in this column.With a YES conclusion, the team leader, enters CAR # in the last column and prepares and issues a Corrective Action Request to the individual responsible for the process step.
With the determination, implementation and monitoring of controls needed to mitigate the effects of the hazards and their risks; the risk management loop is completed with improvements in health and safety performance which results in workplaces that are safer and healthier.
Reporting
The completed Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Determining of Controls worksheets provide a report with the details on how you manage the health and safety risks for your organization.




